Week 3 Pregnancy: Conception, Implantation Begins & What to Expect
Discover what happens in Week 3 of pregnancy, including fertilization, early embryo development, possible symptoms, and essential care tips.
The Comprehensive Clinical Analysis of Human Gestation: Week 3 Developmental Paradigms
The third week of pregnancy is a major biological turning point. This is when your body moves from just getting ready to actually starting a new life. During this week, fertilization and implantation happen with extraordinary detail, even though you might not feel it yet. This report looks at how cells grow, how hormones change, and what you need to eat to stay healthy.
The Start of Life: Fertilization and the Zygote
The story of the third week begins when a sperm meets an egg. This usually happens in the fallopian tube shortly after an egg is released from the ovary. Even before this moment, Your Body's Busy Preparing! By thickening the lining of the womb, your system is creating a perfect environment to nurture a tiny life. To understand how your body laid the groundwork for this, you can look back at the(week 1 pregnancy guide early signs cycle changes and preparation ) for a look at early cycle changes.
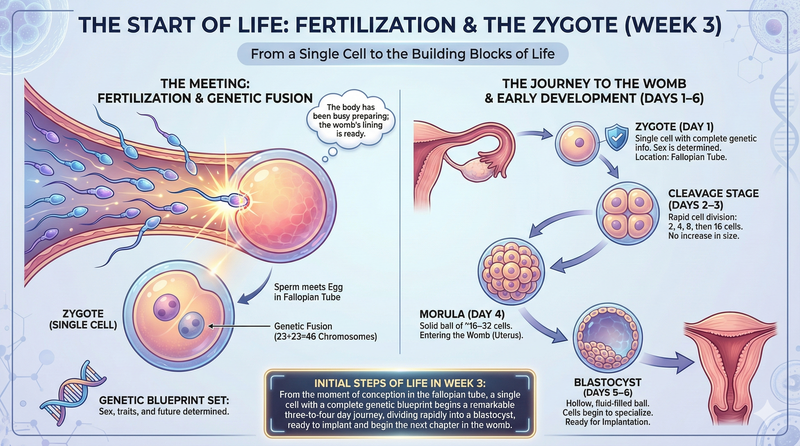
When one sperm gets inside the egg, they fuse together to create a single cell called a zygote. This zygote holds all the instructions for the baby’s future. It has 46 chromosomes—23 from each parent. This "genetic blueprint" decides everything from the baby's biological sex to their physical traits.
As soon as they meet, the zygote creates a shield to keep other sperm out. Then, The Fertilized Egg is Dividing! It begins a process of rapid multiplication, going from 1 cell to 2, then 4, and so on. While this is happening, the tiny cluster of cells travels toward the womb, a trip that takes about three to four days.
Initial Steps of Life in Week 3:
- Zygote (Day 1): A single cell with all the genetic info; the sex is already set. This happens in the fallopian tube.
- Cleavage Stage (Days 2–3): The cell quickly divides into 2,4,8, and then 16 cells.
- Morula (Day 4): A solid ball of about 16–32 cells that looks like a tiny berry. It is now entering the womb.
- Blastocyst (Days 5–6): A hollow, fluid-filled ball where cells start to take on special jobs.
Changing Shape: Moving to the Womb

As the cluster of cells moves, it changes from a solid ball into a more complex shape called a blastocyst. Inside, it separates into two groups. The inner cells will become the baby (the embryo), and the outer cells will become the placenta. Even at this microscopic stage, The Future Is Already Shaping! as the foundations for every organ and system are being laid.
The blastocyst is incredibly tiny—about the size of a pinhead or a period at the end of a sentence. It moves through the tube with the help of tiny hairs and gentle muscle movements. This journey is timed perfectly so the embryo reaches the womb just when the lining is ready for it to "snuggle" in.
Implantation: Finding a Home
Implantation is when the blastocyst attaches itself to the thick, nutrient-rich lining of the womb. This usually starts between 6 and 10 days after the egg was fertilized.
The process happens in three steps:
- Finding a spot: The blastocyst picks a good place on the wall of the womb.
- The "Handshake": The embryo and the mother's body send signals to each other to make sure they are a good match.
- Settling in: The embryo burrows deep into the lining to connect to the mother's blood supply.
This connection is the baby’s life-support system. Once it is tucked in safely, your body starts making special hormones that tell your brain to stop your period and focus on the pregnancy.
Hormones Are on the Rise!

As soon as the embryo settles in, your body starts a surge to protect the new life. The most important one is hCG, often called the "pregnancy hormone". You can find more details about these biological shifts on the(pregnancy ).
Main Hormones in Week 3:
- hCG (from the developing placenta): This tells your body to keep making the other hormones needed for pregnancy. This is what a pregnancy test looks for.
- Progesterone (from the ovary): This keeps the lining of the womb thick and prevents you from having a period. It can make you feel tired or bloated.
- Estrogen (from the ovary): This helps the womb grow and increases blood flow. It might cause mood swings or a stronger sense of smell.
It takes a little while for hCG to build up in your body. This is why testing too early might give a negative result even if you are pregnant.
You May Feel a Little Different!
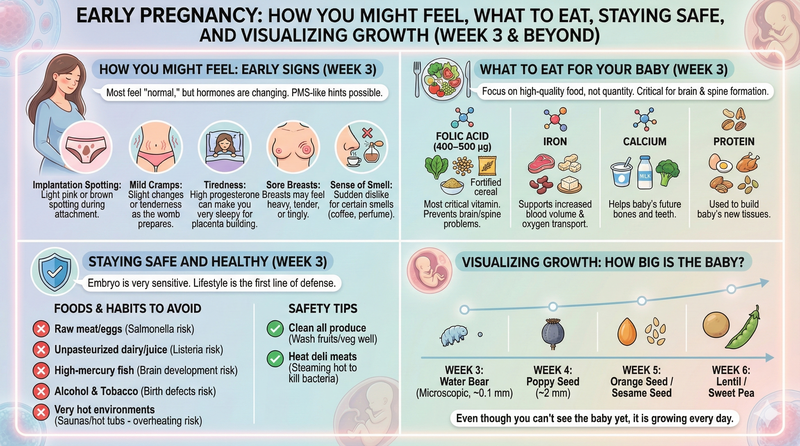
Most people feel "normal" in week 3, but your body is working hard behind the scenes. Because your hormones are changing, You May Feel a Little Different! as you might notice some small "PMS-like" hints.
Common Early Signs:
- Implantation Spotting: You might see light pink or brown spotting when the embryo attaches to the womb.
- Mild Cramps: You may feel a little different, like having mild cramps or tenderness as your womb begins to change.
- Tiredness: High levels of progesterone can make you feel very sleepy as your body builds the placenta.
- Sore Breasts: Your breasts might feel heavy, tender, or tingly.
- Sense of Smell: You might suddenly dislike certain smells, like coffee or perfume.
What to Eat for Your Baby
In week 3, it’s not about eating "twice as much" but about eating high-quality food. Your baby's brain and spine are already starting to form, so certain vitamins are very important.
Important Nutrients and Recipe Ideas:
- Folic Acid (400–500μg): This is the most critical vitamin for preventing brain and spine problems. For a nutritious breakfast, try these(nutritious banana oatmeal pancakes.
- Iron: Your body needs more blood now to carry oxygen to the embryo. Protein-rich(simple boiled eggs are an easy way to boost your intake.
- Calcium: This helps the baby’s future bones and teeth. You can find more calcium-rich ideas among our(recipes.
- Protein: Used to build the baby's new tissues. Explore our(colorful rainbow recipes kids for fun, nutrient-dense meal ideas.
Staying Safe and Healthy
Because cells are dividing so fast, the embryo is very sensitive this week. Your lifestyle choices are its first line of defense. You can find more safety guidelines in our(https://kidypulse.com/us/blog/healthy-parenting).
Foods and Habits to Avoid:
- Raw or undercooked meat and eggs: These can carry germs like Salmonella that are dangerous for the baby.
- Unpasteurized dairy or juice: These can have Listeria, which is a risk for miscarriage.
- High-mercury fish: These can hurt the baby's developing brain.
- Alcohol and Tobacco: These should be avoided completely to prevent birth defects.
- Very hot environments: Stay away from saunas and hot tubs, as overheating can cause problems for the baby's spine.
Visualizing Growth: How Big is the Baby?
Even though you can't see the baby yet, it is growing every day. You can learn more about this incredible process in our guide to Mind-blowing facts about your child’s growing brain and body.
Size Comparisons as the Baby Grows:
- Week 3: About the size of a "water bear" (a microscopic creature), roughly 0.1 mm.
- Week 4: The size of a poppy seed, roughly 2 mm.
- Week 5: The size of an orange seed or sesame seed.
- Week 6: The size of a lentil or a sweet pea.
Summary and Next Steps
The third week is the hidden foundation of your pregnancy. Even if you only feel a little different, your body is doing incredible work to shape the future. To support your emotional and cognitive growth during this time, consider reviewing our Expert parenting tips for growth.
To stay on track:
- Keep taking your prenatal vitamins with folic acid.
- Drink plenty of water and get extra rest when you can.
- Eat a variety of healthy, colorful foods.
- Wait until you've missed your period to take a pregnancy test for the most accurate result.
Your body is quietly preparing for the next stages, and every small change is a step on this amazing journey.

Comments
No comments yet. Be the first to leave a comment!